[TOC]
ABE
访问结构
与门结构
访问控制树
LSSS
ABE存在的问题
(1) CP-ABE机制中的策略由消息发送方制定,使得系统公钥设计的复杂性与策略复杂性相关,限制了访问结构的设计;
(2) ABE 机制中用户密钥与属性相关,属性的动态性增加了密钥撤销 的开销和难度;
(3) ABE 机制中用户私钥由授权机构产生,且用户私钥与用户的隐私信息(如 ID)无关,造成了授 权机构和用户都可能泄露用户私钥,无法分清密钥泄露的责任;
(4) 多机构 ABE 能够分担授权机构的责任,也满 足分布式应用的多机构协作的需求
椭圆曲线加密
https://switch-router.gitee.io/blog/ecc/
 时间复杂度按照二进制算法
时间复杂度按照二进制算法
def bits(n):
while n:
yield n & 1
n >>= 1
def double_and_add(n, x):
"""
Returns the result of n * x, computed using
the double and add algorithm.
"""
result = 0
addend = x // P点
for bit in bits(n):
if bit == 1:
result += addend
addend *= 2
return result
如果倍乘和加法都是时间复杂度为常数的运算,那么这个算法的时间复杂度是O(logn)。(或者是O(k),k是比特长度的话),这个结果还是非常好的。
双线性映射
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100636577
e: G1 × G2 → GT
Bilinear groups are the basis of many of the new cryptographic protocols. They consist of a triplet of groups (G₁, G₂ and GT) such that there exists a function e(G1x,G2y)=GTxy(where gₓ is a generator of the respective group). That function is called a pairing function.
e(3, 4 + 5) = 2³˙⁹ = 2²⁷
e(3, 4) * e(3, 5) = 2³˙⁴ * 2³˙⁵ = 2¹² * 2¹⁵ = 2²⁷.
例: 通过 pairing 证明您知道 x² - x - 42 = 0 的解, 然而并不透露这个解的具体数值.
答: 如果 e(G, G)k = 1 成立, 那么 k 必须为 0 或者目标群的倍数. 因此, 如果存在 e(G, G)x² - x - 42 , 我们可以确定原始二次方程式成立. 使用双线性性重写方程 e(G, G)x² ⋅ e(G, G)-x ⋅ e(G, G)-42 = 1, 进一步的 e(xG, xG) ⋅ e(xG, -G) ⋅ e(G, -42G) = 1. 因此, 我们只需要提供 xG 的值. 同时由于椭圆曲线的离散对数问题, 从 xG 反推回 x 是困难的.
双线性映射在ABE中的使用是通过将属性映射到椭圆曲线上的点,并利用双线性性质来实现访问策略的验证和解密操作。
元素的阶 一个群内的一个元素a的阶(有时称为周期)是指会使得am = e的最小正整数m(其中的e为这个群的单位元素,且am为a的m次幂)。若没有此数存在,则称a有无限阶。有限群的所有元素都有有限阶。
cpabe
https://acsc.cs.utexas.edu/cpabe/ 设 G0 是素阶 p 的双线性群,设 g是G0的生成元,G0×G0→ G1 表示双线性映射。安全参数 κ 将确定组的大小。
参考 cpabe python实现 https://jhuisi.github.io/charm/_modules/abenc_bsw07.html#main
访问控制树实现 https://jhuisi.github.io/charm/toolbox/secretutil.html
setup
生成元 椭圆曲线上所有点加上O包含了很多循环子群(cyclic subgroups), 循环子群中的生成元(Generator)也被称作素元(primitive element),通过不断自加,它可以“生成”群众其他所有元素,就是椭圆曲线上的一个点P,通过不断自加,它可以生成椭圆曲线上所有点。 即椭圆曲线上 = P、2P、3P、….nP,其中n为循环子群的阶。生成元是椭圆曲线上的点
PK = G0,g,h = gβ,f = g1/β,e(g,g)α MK = (β, gα)
加密
访问树 T: 设 T 是表示访问结构的树。树的每个非叶节点代表一个阈值门,由其子节点和阈值描述。如果 numx 是节点 x 的子节点数,kx 是其阈值,则 0 < kx ≤ numx。当 kx = 1 时,阈值门是一个或门,当 kx = numx 时,它是一个与门。树的每个叶节点 x 由一个属性和一个阈值 kx = 1 来描述。 为了便于使用访问树,定义了一些函数。我们用 parent(x) 表示树中节点 x 的父节点。仅当 x 是叶节点时才定义函数 att(x),并表示与树中叶节点 x 关联的属性。访问树 T 还定义了每个节点的子节点之间的顺序,即节点的子节点从 1 到 num 编号。函数 index(x) 返回与节点 x 关联的数字。其中索引值以任意方式唯一分配给给定键的访问结构中的节点。
Each interior node of the tree is a threshold gate and the leaves are associated with attributes. (We note that this setting is very expressive. For example, we can represent a tree with “AND” and “OR” gates by using respectively 2 of 2 and 1 of 2 threshold gates.) A user will be able to decrypt a ciphertext with a given key if and only if there is an assignment of attributes from the private key to nodes of the tree such that the tree is satisfied. We use the same notation as [15] to describe the access trees, even though in our case the attributes are used to identify the keys (as opposed to the data).
加密过程 (其中dx是每个节点的阶)每个叶子都是多项式构造的阈值门,加密过程的访问控制树构造,从根节点R开始,算法选择一个随机的s∈Zp,并设置qR(0)=s。然后,它随机选择多项式qR的其他dR点来完全定义它。对于任何其他节点x,它设置qx(0)=qparent(x)(index(x)),并随机选择dx其他点来完全定义qx。
让,Y是T中叶子节点的集合。然后,通过给出树状访问结构T并计算出密码文本,构建出密码文本
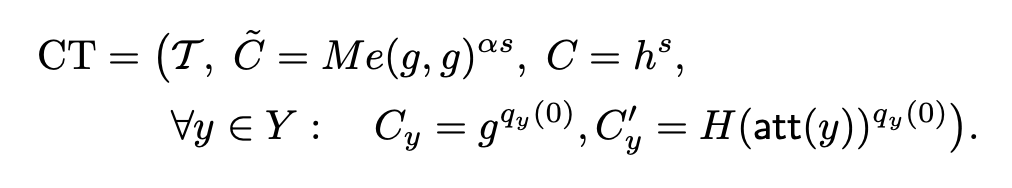
- T是访问控制树
- C’ = 密文 * e(g,g)αs,其中e(g,g)α来自公钥
- C = hs,h = gβ来自公钥
- Cy和 C’y 是在G0上对访问控制树的加密
@Input(pk_t, GT, str)
@Output(ct_t)
def encrypt(self, pk, M, policy_str):
policy = util.createPolicy(policy_str)
a_list = util.getAttributeList(policy)
s = group.random(ZR)
shares = util.calculateSharesDict(s, policy)
C = pk['h'] ** s
C_y, C_y_pr = {}, {}
for i in shares.keys():
j = util.strip_index(i)
C_y[i] = pk['g'] ** shares[i]
C_y_pr[i] = group.hash(j, G2) ** shares[i]
return { 'C_tilde':(pk['e_gg_alpha'] ** s) * M,
'C':C, 'Cy':C_y, 'Cyp':C_y_pr, 'policy':policy_str, 'attributes':a_list }
KeyGen(MK, S )
\(SK = (D = g^{(α+r)/β},∀j∈S: D_j=g^r·H(j)^{r_j},D'_j=g^{r_j}).\)
@Input(pk_t, mk_t, [str])
@Output(sk_t)
def keygen(self, pk, mk, S):
r = group.random()
g_r = (pk['g2'] ** r)
D = (mk['g2_alpha'] * g_r) ** (1 / mk['beta'])
D_j, D_j_pr = {}, {}
for j in S:
r_j = group.random()
D_j[j] = g_r * (group.hash(j, G2) ** r_j)
D_j_pr[j] = pk['g'] ** r_j
return { 'D':D, 'Dj':D_j, 'Djp':D_j_pr, 'S':S }
Decrypt(CT,SK)
@Input(pk_t, sk_t, ct_t)
@Output(GT)
def decrypt(self, pk, sk, ct):
policy = util.createPolicy(ct['policy'])
pruned_list = util.prune(policy, sk['S'])
if pruned_list == False:
return False
z = util.getCoefficients(policy)
A = 1
for i in pruned_list:
j = i.getAttributeAndIndex(); k = i.getAttribute()
A *= ( pair(ct['Cy'][j], sk['Dj'][k]) / pair(sk['Djp'][k], ct['Cyp'][j]) ) ** z[j]
return ct['C_tilde'] / (pair(ct['C'], sk['D']) / A)
